IPython各種用法 - 讀書筆記 - Python Data Science Handbook - Python數據科學 - 寫程式非常重要的性能測算與計時 - IPython的相關網路資源與書籍 - 筆記#3

1.7章 程式性能的測算與計時
1.IPython中的各種計算性能方法
- %time: 測量單個語句的執行時間
- %timeit: 重複測量單個語句的執行時間,並計算平均時間,來取得更準確的執行時間結果
- %prun: 使用性能計算工具與程式碼一起執行
- %lprun: 使用單個語句執行的性能計算工具與程式碼一起運行
- %memit: 計算單個語句佔用的內存(Memory)空間
- %mprun: 使用單個語句執行的內存(Memory)計算工具與程式碼一起執行
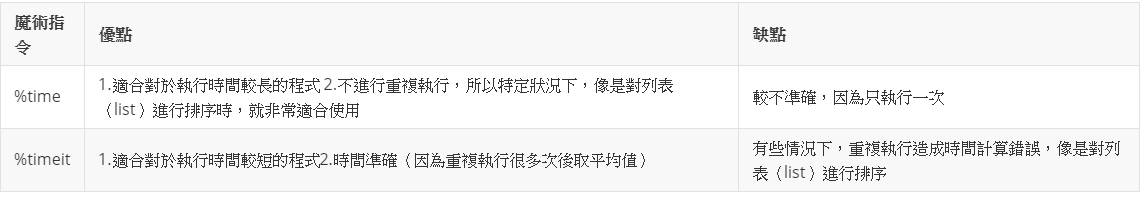
2. %time & %timeit 程式執行計時工具
%timeit
%timeit sum(range(600))
執行結果
7.35 µs ± 38.7 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100000 loops each)
補充說明:由於上面的例子執行速度相當快,所以%timeit會自動重複運行很多回合,但如果換成一個執行較慢的計算,%timeit會自動減少回合數,如下例子
%%timeit total = 0 for i in range(6000): for k in range(6000): total += i * k print(total)
執行結果
323892009000000 323892009000000 323892009000000 323892009000000 323892009000000 323892009000000 323892009000000 323892009000000 2.73 s ± 212 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1 loop each)
狀況:如果遇到列表進行排序操作時,重複執行的結果會誤導我們,因為對一個已經排好序的列表進行排序是非常快的,所以在第一次執行完成後,後面重複進行測量的數據都是錯誤的,時間會不對(會過快)
import random L = [random.random() for i in range(1000000)] %timeit L.sort()
執行結果
21.9 ms ± 278 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1 loop each)
%time
範例一:計算還沒排序的列表
import random
L = [random.random() for i in range(1000000)]
print('Sorting an Unsorting list(L)')
%time L.sort()
執行結果
Sorting an Unsorting list(L) Wall time: 230 ms
範例二:接著上面執行計算已經排好序的列表
print('Sorting an Alreaddy Sorted list(L)')
%time L.sort()
執行結果
Sorting an Alreaddy Sorted list(L) Wall time: 22.7 ms
可以明顯看出時間差異!!所以非常不適合重複執行!!
計時 - %timeit為什麼通常都比%time的執行時間快?
%timeit會有一種額外的機制,來防止系統調用(System calls)影響程式執行的時間結果,像是它會防止系統清理掉不再使用的Python物件(又稱垃圾收集),才不會讓這樣的狀況影響執行的時間
% 只能執行一行程式碼,%%就可以執行一整段程式碼
%%time total = 0 for i in range(6000): for k in range(6000): total += i * k print(total)
執行結果
323892009000000 Wall time: 5.01 s
3. %prun整個Python檔的性能測算
舉例:先自行定義一個函數,然後測算它的性能
In [1]: def sum_list(N): ...: total = 0 ...: for i in range(5): ...: L = [j ^ (j >> i) for j in range(N)] ...: return total
計算性能%prun
In [2]: %prun sum_list(10000000)
9 function calls in 6.178 seconds
Ordered by: internal time
ncalls tottime percall cumtime percall filename:lineno(function)
5 5.708 1.142 5.708 1.142 <ipython-input-1-9b46611eb043>:4(<listcomp>)
1 0.355 0.355 6.063 6.063 <ipython-input-1-9b46611eb043>:1(sum_list)
1 0.115 0.115 6.178 6.178 <string>:1(<module>)
1 0.000 0.000 6.178 6.178 {built-in method builtins.exec}
1 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 {method 'disable' of '_lsprof.Profiler' objects}
產出的結果表格,顯示每個函數調用的執行時間排序(從大到小),當然從我們的範例中,因為只有執行一個函數,所以耗時最長的就是sum_list
使用%prun就能看出程式在哪耗時最久,也就能知道要從哪裡著手了
4. %lprun 一行一行的執行程式碼去測試性能
安裝第三方套件到Python中
pip install line_profiler
再從IPython中載入套件
%load_ext line_profiler
執行%lprun來計算函數的逐條程式性能
%lprun -f sum_list(5000)
書本說從結果可以看出,%lprun會幫我們一行一行計算程式性能,單位是毫秒,讓我們知道哪一行執行時間最久,就能根據這個資訊優化哪行程式
這邊我在安裝第三方套件的時候一直報錯,所以沒辦法親自試試,大家可以自行使用看看
5. %memit & %mprun 計算內存(Memory)使用量
安裝第三方套件到Python中
pip install memory_profiler
再從IPython載入套件
%load_ext memory_profiler
%memit 整個程式的內存空間(Memory Space)使用量
執行%memit來計算函數的逐條程式性能
In [1]: %load_ext memory_profiler In [2]: def sum_list(N): ...: ...: total = 0 ...: ...: for i in range(5): ...: ...: L = [j ^ (j >> i) for j in range(N)] ...: ...: return total ...: In [3]: %memit sum_list(6000) peak memory: 50.06 MiB, increment: 0.51 MiB
結果:從peak memory可以看出這個程式用了多少的內存(Memory)空間
%mprun - 逐行程式檢視內存(Memory)空間的使用量
- 限制:它只能在獨立的模塊(Modules)上使用,不能應用在notebook本身,簡單來說,它要執行整個外部的Python檔
- 使用%%file,來創建一個Python檔,如果遇到Permission denied,表示權限不夠喔,可以建議改用Anaconda Powershell Prompt 或是自行用別的編譯器來創建Python檔
In [3]: %memit sum_list(6000) peak memory: 50.06 MiB, increment: 0.51 MiB In [4]: %%file mprun_demo_example.py ...: def sum_lists(N): ...: total = 0 ...: for i in range(6): ...: L = [j ^ (j >> i) for j in range(N)] ...: total += sum(L) ...: del L ...: return toal ...: Writing mprun_demo_example.py
- 導入模塊,也就是導入外部Python檔(前面所建立的),並使用內存空間(Memory Space)計算工具 - %mprun,來進行逐行程式碼計算
In [5]: from mprun_demo_example import sum_lists In [6]: %mprun -f sum_lists sum_lists(10000000)
執行結果
Line # Mem usage Increment Occurences Line Contents ============================================================ 1 51.3 MiB 51.3 MiB 1 def sum_lists(N): 2 51.3 MiB 0.0 MiB 1 total = 0 3 51.3 MiB 0.0 MiB 2 for i in range(6): 4 359.6 MiB -75619584.5 MiB 17985287 L = [j ^ (j >> i) for j in range(N)] 5 127.6 MiB 0.0 MiB 1 total += sum(L) 6 51.3 MiB -76.3 MiB 1 del L 7 return toal *** KeyboardInterrupt exception caught in code being profiled.
- Increment 表示內存空間(Memory Space)是如何變化的,創建L串列,與最後刪除L串列,大家可以看出內存的佔用與釋放變化
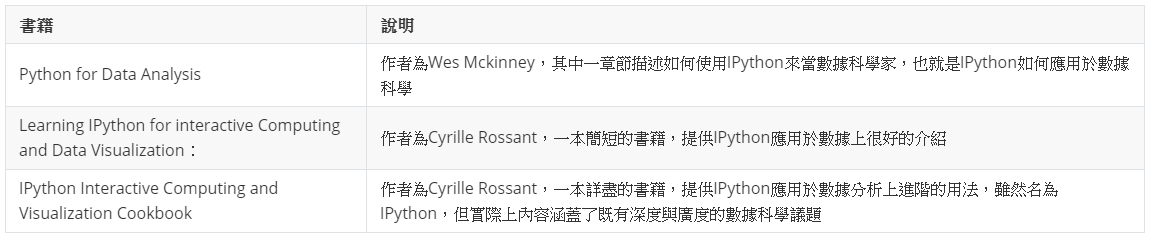
1.8章 IPython網路資源與相關數據推薦
1. 網路資源
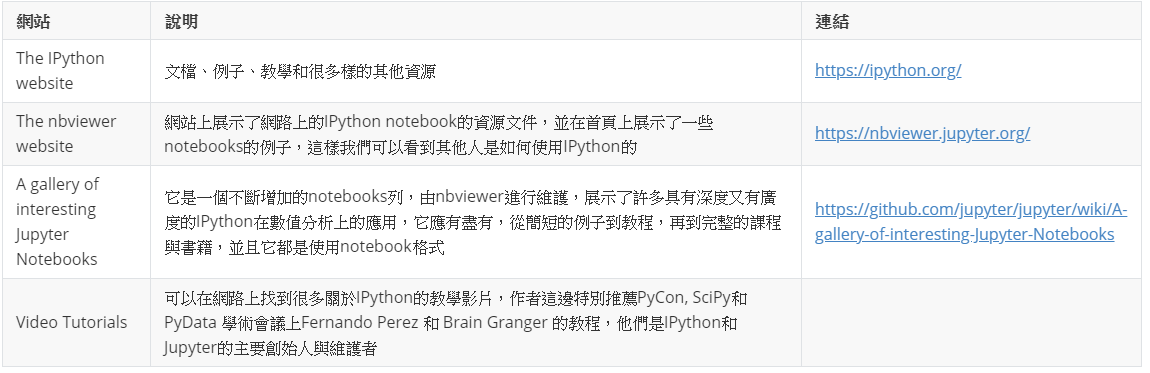
2. 相關書籍