Gibbs Reflective Cycle in Education: Enhancing Teaching Practices
Reflective practice is a cornerstone of professional development in education. Among the various models available, the Gibbs Reflective Cycle stands out as a practical and structured framework. Developed by Graham Gibbs in 1988, this model encourages educators to think systematically about the phases of an experience, fostering continuous learning and improvement in teaching practices.
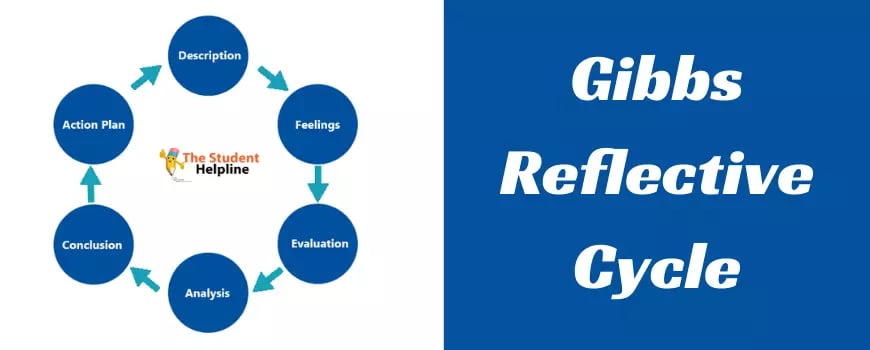
What is Gibbs Reflective Cycle?
Gibbs Reflective Cycle is a six-step model designed to guide individuals through a reflective process. The steps are:
Description: What happened?
Feelings: What were you thinking and feeling?
Evaluation: What was good and bad about the experience?
Analysis: What sense can you make of the situation?
Conclusion: What else could you have done?
Action Plan: If it arose again, what would you do differently?
By addressing each of these steps, educators can gain a deeper understanding of their experiences and identify ways to enhance their teaching effectiveness.
Importance of Reflection in Education
Encourages self-awareness.
Promotes adaptive learning.
Helps identify strengths and areas for improvement.
Fosters a culture of continuous professional development.
Incorporating Gibbs Reflective Cycle in educational settings enables teachers to critically analyze their teaching practices, ultimately improving student outcomes.
Applying Gibbs Reflective Cycle in Teaching Practices
1. Description
Begin by recounting a specific teaching experience. For example, consider a lesson that did not go as planned or a moment of student engagement that stood out. Include essential details such as the lesson topic, classroom environment, and student reactions.
2. Feelings
Reflect on your emotions during the experience. Were you frustrated, pleased, or uncertain? Understanding your feelings can provide insight into your responses and decision-making during the lesson.
3. Evaluation
Assess the experience objectively. Identify what aspects went well and which areas could have been improved. For instance, did students grasp the concept, or were there signs of confusion? This step helps distinguish effective strategies from those that need refinement.
4. Analysis
Delve deeper into the underlying factors that influenced the experience. Did the instructional method suit the topic? Were there external factors, such as time constraints or classroom dynamics, that played a role? Linking theory to practice can also enhance your understanding.
5. Conclusion
Summarize the key lessons learned. Reflect on alternative approaches that might have led to a more favorable outcome. For instance, could incorporating technology or varying instructional methods have made a difference?
6. Action Plan
Formulate a plan for future teaching practices. Specify actionable steps to address identified areas of improvement. For example, you might decide to integrate more interactive activities or seek peer feedback on lesson plans.
Benefits of Using Gibbs Reflective Cycle in Education
Structured Reflection: The step-by-step approach ensures comprehensive analysis.
Enhanced Problem-Solving Skills: Identifying root causes fosters effective solutions.
Improved Student Engagement: Reflective practices lead to more engaging and effective teaching strategies.
Professional Development: Continuous reflection aligns with lifelong learning goals.
Real-Life Example: Implementing Gibbs Reflective Cycle
Scenario:
A science teacher notices that students struggled to engage with a complex topic during a lesson.
Reflection Using Gibbs Cycle:
Description: The topic was photosynthesis, and many students appeared disengaged.
Feelings: The teacher felt frustrated and concerned about student comprehension.
Evaluation: While the presentation was clear, it lacked interactive elements.
Analysis: Passive learning methods might have contributed to the lack of engagement.
Conclusion: Incorporating hands-on experiments or visual aids could enhance understanding.
Action Plan: Plan future lessons with interactive models and real-world applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is Gibbs Reflective Cycle used for in education?
Gibbs Reflective Cycle helps educators systematically evaluate their teaching practices, identify areas for improvement, and enhance student outcomes through structured reflection.
2. How can teachers integrate Gibbs Reflective Cycle into their routine?
Teachers can integrate the cycle by dedicating time for reflection after each lesson, maintaining a reflective journal, or participating in peer discussions to share insights and feedback.
3. Can Gibbs Reflective Cycle be used for group reflections?
Yes, the cycle is highly effective for group reflections. Teams can collaboratively analyze shared experiences, promoting collective learning and professional growth.
4. How does Gibbs Reflective Cycle improve teaching practices?
By fostering a habit of critical reflection, the cycle helps teachers recognize effective strategies, address challenges, and develop innovative approaches to teaching.
5. Are there any challenges in using Gibbs Reflective Cycle?
Some challenges include finding time for reflection amidst a busy schedule and the potential difficulty in objectively evaluating one's own practices. However, these challenges can be mitigated with consistent effort and supportive peer networks.
Conclusion
Gibbs Reflective Cycle is an invaluable tool for educators aiming to refine their teaching practices. By systematically reflecting on experiences, teachers can uncover insights that drive professional growth and improve student outcomes. In the ever-evolving field of education, adopting reflective practices ensures that educators remain adaptive, effective, and inspired to foster meaningful learning experiences.
喜欢我的作品吗?别忘了给予支持与赞赏,让我知道在创作的路上有你陪伴,一起延续这份热忱!

- 来自作者
- 相关推荐